Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets heart takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
1.
Overview
The heart is a vital organ that plays a central role in the circulatory system. It is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood throughout the body and removing deoxygenated blood. The heart’s importance has been recognized since ancient times, and its medical understanding has evolved significantly over the centuries.
2.
Anatomy
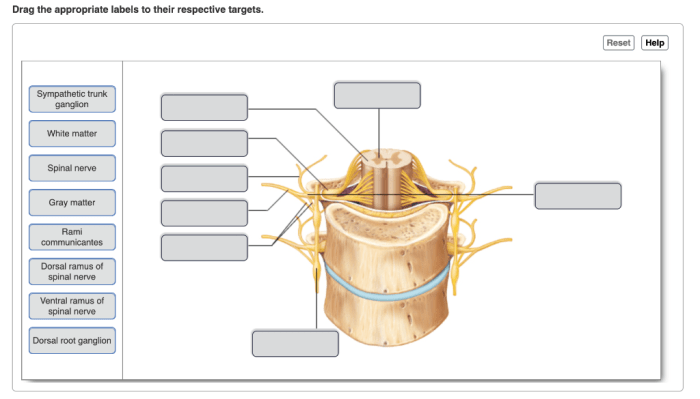
Chambers of the Heart
| Chamber | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Right Atrium | Receives deoxygenated blood from the body | Upper right chamber |
| Right Ventricle | Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs | Lower right chamber |
| Left Atrium | Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs | Upper left chamber |
| Left Ventricle | Pumps oxygenated blood to the body | Lower left chamber |
Valves of the Heart
The heart contains four valves that prevent backflow of blood: the tricuspid valve, pulmonary valve, mitral valve, and aortic valve. These valves ensure that blood flows in the correct direction and maintain proper pressure within the heart.
3.
Physiology
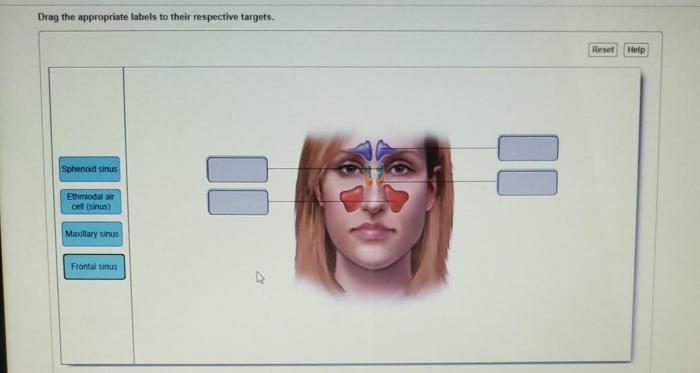
Electrical System of the Heart
The heart’s electrical system coordinates the contraction of its chambers. The sinoatrial (SA) node generates electrical impulses that spread through the atrioventricular (AV) node and Purkinje fibers, causing the heart to beat in a rhythmic manner.
Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle refers to the sequence of events that occur during each heartbeat. It consists of systole, when the heart contracts and pumps blood, and diastole, when the heart relaxes and fills with blood.
4.
Heart Conditions
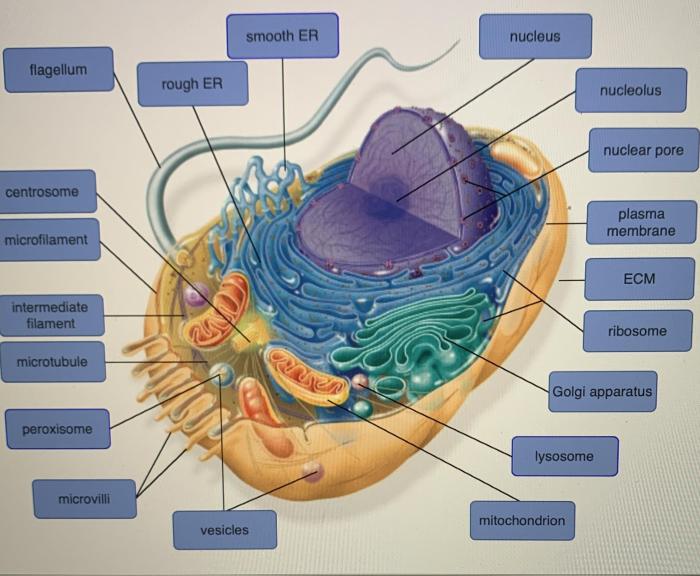
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD) occurs when the arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle. Symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
Heart Failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart cannot pump blood effectively. This can lead to fluid buildup in the lungs and other organs, resulting in shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and ankles.
Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias are irregular heart rhythms that can cause the heart to beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly. Symptoms include palpitations, chest pain, and dizziness.
5.
Heart Health
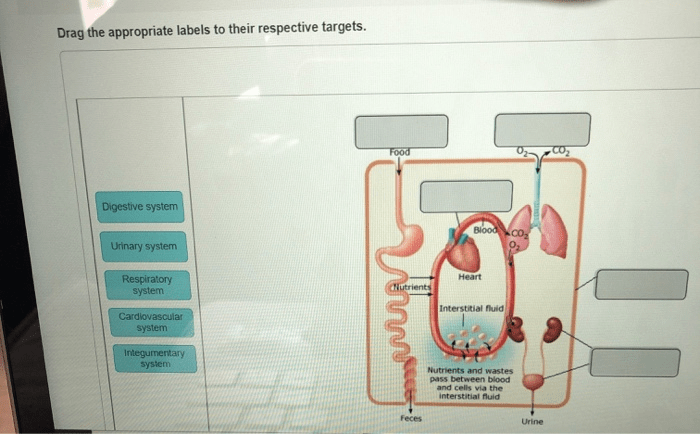
Maintaining a Healthy Heart
Maintaining a healthy heart involves lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management. Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium can help reduce the risk of heart disease.
Regular Heart Checkups
Regular heart checkups are essential for detecting and managing heart conditions early. These checkups may include blood pressure measurements, electrocardiograms (ECGs), and echocardiograms.
FAQ Insights: Drag The Appropriate Labels To Their Respective Targets Heart
What is the heart?
The heart is a vital organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
What are the four chambers of the heart?
The four chambers of the heart are the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
What is the function of the heart?
The function of the heart is to pump blood throughout the body.